Hearing Loss & Deafness
Overview
Hearing loss results from the interruption of sound transmission, which is a complex process involving the external, middle, and inner ear, as well as the vestibulocochlear nerve, brainstem, and cerebral cortex.
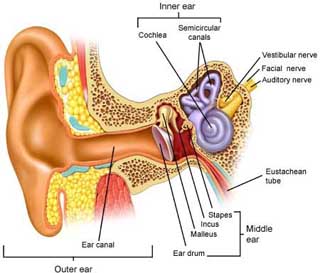
This motion is converted to neural impulses at the auditory nerve, which are then transmitted through the brainstem to the auditory cortex for processing. Sound intensity is determined by a complex interaction of inner and outer hair cells. Sound frequency is determined by the interplay between the dynamic properties of the basilar membrane and that of the surrounding fluid. [Moller: 2012] Dysfunction in any component of this system can result in hearing loss.
Hearing loss may be syndromic (associated with other genetic, medical, or anatomic problems) or non-syndromic (lacking such associations). The distinction between syndromic and non-syndromic may change with the age of the child. For example, children with Usher syndrome may initially be thought to have non-syndromic hearing loss but, as the associated retinitis pigmentosa becomes apparent with age, the syndromic diagnosis becomes apparent. The onset of hearing loss may be congenital (present at birth), prelingual (before the development of speech), or of later onset. Hearing loss at any age may be due to a variety of factors including genetic variations, infection, trauma, etc. Hearing loss may also be grouped into types, related to the cause or mechanism of the loss, the ranges of severity, described by the decibels below which the child cannot hear or discriminate sounds, and the pattern of alteration by frequency on the audiogram. These groupings are detailed below under Clinical Classification. [Lieu: 2020] provides a current and comprehensive review of hearing loss in children.
As hearing loss severity increases, more speech sounds fall below the level of detection causing greater difficulty in communication. Quiet conversation, which averages 30 dB, can be difficult to understand for individuals with even mild hearing loss. Normal conversation, which averages 50 dB, is below the hearing level of some individuals with moderate hearing loss, and even loud conversation, which averages 70 dB, is below the hearing level of individuals with severe to profound loss.
Deafness is often defined as any degree of hearing loss that sufficiently reduces the intelligibility of speech or interferes with learning. However, many professionals reserve the term ‘deafness’ to describe a severe to profound hearing loss.
Other Names & Coding
H90.0, Conductive hearing loss, bilateral
H90.1x, Conductive hearing loss, unilateral with unrestricted hearing on the contralateral side
H90.2, Conductive hearing loss, unspecified
H90.3, Sensorineural hearing loss, bilateral
H90.4x, Sensorineural hearing loss, unilateral with unrestricted hearing on the contralateral side
H90.5, Unspecified sensorineural hearing loss
H90.6, Mixed conductive and sensorineural hearing loss, bilateral
H90.7x, Mixed conductive and sensorineural hearing loss, unilateral with unrestricted hearing on the contralateral side
H90.8, Mixed conductive and sensorineural hearing loss, unspecified
H91.0x, Ototoxic hearing loss
H91.3, Deaf nonspeaking, not elsewhere classified
H91.8xx, Other specified hearing loss
H91.9x, Unspecified hearing loss
The symbols x represent additional digits indicating laterality, which are required for billing. See ICD10Data.com for more information and additional codes.
Prevalence
Some children will acquire permanent hearing impairment during the first few years of life; hearing loss of mild or greater severity is reported in approximately 3.1% of children and adolescents nationwide. [Mehra: 2009]
For more detail, click Prevalence of Permanent Congenital Hearing Loss (NCHAM) (
 36 KB).
36 KB).
Genetics
Pathogenic variations in GJB2 are responsible for approximately 10 to 20% of all childhood genetic hearing loss and cause about 50% of the loss with more than one affected child amongst offspring with the same parents. Tests for the common 35delG mutation (single nucleotide deletion at site 35) and complete GJB2 gene sequencing are available clinically and should be offered to families affected by non-syndromic hearing loss of unknown cause. The American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics also recommended consideration of hearing loss gene panel tests using next-generation sequencing testing for children with sensorineural hearing loss of unknown cause. [Alford: 2014] More recently some authors have suggested proceeding to exome sequencing (ES) in the setting of a child with no known cause of the hearing loss or deafness; [Downie: 2021] however obtaining insurance coverage in the US for ES can be more difficult than a gene panel. If there are findings on history and physical exam which suggest a syndromic etiology for hearing loss, directed gene testing for the syndrome is indicated. [Alford: 2014] Currently, the genes known to cause specific syndromes (e.g., PAX3 in Waardenburg syndrome) are available on most commercially available hearing loss gene panels or on specific panels covering the particular genes causing the syndrome. More than 10 commercial or University-based laboratories in North America offer gene panels for hearing loss and deafness that include over 100 or more genes using next-generation sequencing technologies. These laboratories can be accessed through the Genetic Testing Registry.
Common recessive types of hearing loss are Usher syndrome (16 genes, ~3-6% of congenital hearing loss) and SLC16A4-related hearing loss including Pendred syndrome. Common autosomal dominant syndromes causing hearing loss include are Waardenburg syndromes 1-4, branchio-oto-renal (BOR) syndrome, and CHARGE syndrome. All of these syndromes have current comprehensive reviews available in GeneReviews, the open access NIH/NLM online resource (GeneReviews (NLM)).
Prognosis
Practice Guidelines
Joint Committee on Infant Hearing.
Year 2019 position statement: Principles and guidelines for early hearing detection and intervention programs.
Journal of Early Hearing Detection and Intervention.
2019.
/ Full Text
US Preventive Services Task Force.
Universal screening for hearing loss in newborns: US Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement.
Pediatrics.
2008;122(1):143-8.
PubMed abstract
Harlor AD Jr, Bower C.
Hearing assessment in infants and children: recommendations beyond neonatal screening.
Pediatrics.
2009;124(4):1252-63.
PubMed abstract / Full Text
Alford RL, Arnos KS, Fox M, Lin JW, Palmer CG, Pandya A, Rehm HL, Robin NH, Scott DA, Yoshinaga-Itano C.
American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics guideline for the clinical evaluation and etiologic diagnosis of hearing
loss.
Genet Med.
2014;16(4):347-55.
PubMed abstract
Liming BJ, Carter J, Cheng A, Choo D, Curotta J, Carvalho D, Germiller JA, Hone S, Kenna MA, Loundon N, Preciado D, Schilder
A, Reilly BJ, Roman S, Strychowsky J, Triglia JM, Young N, Smith RJ.
International Pediatric Otolaryngology Group (IPOG) consensus recommendations: Hearing loss in the pediatric patient.
Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol.
2016;90:251-258.
PubMed abstract
Roles of the Medical Home
Clinical Assessment
Overview
The JCIH 2007 Position Statement recommends screening all newborns for hearing loss by 1 month of age, diagnostic audiologic evaluation by 3 months of age for those who fail screening, and early intervention with complete medical evaluation by 6 months of age for those with hearing loss. [Joint: 2019] This approach has been referred to as the 1-3-6 Newborn Hearing Checklist (AAP) (
 105 KB).
105 KB).Many cases of permanent sensorineural hearing loss are detected with universal hearing screening in the newborn nursery. However, hearing loss may develop after the perinatal period (late-onset) or be progressive in nature. Regardless of a normal newborn screening result, any child with suspected hearing loss and/or language or other developmental delay should be assessed for hearing loss since early intervention is critical to optimal language and cognitive development.
Pearls & Alerts for Assessment
Repeat hearing screen for readmitted infantsFor infants readmitted to the hospital during the first month of life for conditions known to be associated with hearing loss (hyperbilirubinemia requiring exchange transfusion, culture positive sepsis, bacterial meningitis, congenital cytomegalic virus (CMV) syndrome), repeat hearing screening is recommended prior to discharge.
When a newborn screen is unavailableNewborn hearing screening may not be completed with home births or births at centers not offering screening, and occasionally infants will be discharged to home prior to its completion. In these cases, referral should be made for outpatient hearing screening as soon as possible and no later than 1 month of age.
Infants with prolonged NICU stays (>5 days) are at increased risk for auditory neuropathyThis type of hearing loss may not be evident on otoacoustic emission testing. These infants should have an automated ABR or more formal diagnostic ABR testing as part of their initial hearing screen, with formal audiologic assessment for those who do not pass.
Screening
For the Condition
- Caregiver concern regarding hearing, speech, language, or developmental delay
- Family history of permanent childhood hearing loss
- Neonatal intensive care of more than 5 days or, regardless of length of stay, history of: extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO), assisted ventilation, exposure to ototoxic antibiotics (gentamicin and tobramycin) or loop diuretics (furosemide), or hyperbilirubinemia requiring exchange transfusion
- Intrauterine infections such as cytomegalovirus (CMV), herpes, rubella, syphilis, and toxoplasmosis. CMV-related hearing loss is often progressive and may develop after the neonatal period. Fluctuating hearing loss is also common. Children with asymptomatic congenital CMV infection should have hearing screens at birth and then regular testing through school age. In Utah, testing is recommended every 3 months until 3 years of age then every 6 months until 6 years than annually afterwards.
- Conditions associated with hearing loss, such as neurofibromatosis type 2, osteopetrosis, and syndromes such as Usher, Waardenburg, CHARGE, Alport, Pendred, and Jervell and Lange-Nielson
- Neurodegenerative disorders, such as Hunter syndrome, or sensory motor neuropathies, such as Friedreich ataxia and Charcot-Marie-Tooth syndrome [Harlor: 2009]
- Culture-positive postnatal infections associated with sensorineural hearing loss, including confirmed bacterial and viral (especially herpes viruses and varicella) meningitis
- Head trauma, especially basal skull/temporal bone fracture that requires hospitalization
- Chemotherapy
- Recurrent/persistent otitis media
Of Family Members
For Complications
Screening with electrocardiogram (EKG) for Jervell and Lange-Nielsen Syndrome (GeneReviews), a potentially lethal syndromic hearing loss associated with prolonged QT syndrome, should be considered for infants with bilateral profound sensorineural hearing loss or a positive family history of prolonged QT interval, syncope, or sudden cardiac death.
Presentations
- Parental/caregiver concern for hearing loss
- Language/communication delay or unusual quality of voice
- Behavioral concerns, such as inattentiveness, poor listening, hyperactivity, or tantrums
- Decline in school performance
Clinical Classification
- Congenital, prelingual, or later-onset hearing loss is based on age of diagnosis
- The causes of hearing loss are classified as genetic, environmental, and cryptogenic (unknown etiology)
- Sensorineural hearing loss (SNHL) results from disorders of the cochlea, often involving the hair cells.
- Conductive hearing loss (CHL) results from interference with the transmission of sound vibrations through the middle to the inner ear. Although this condition causes less than 20% of hearing loss in the general population, CHL causes a higher proportion of pediatric cases (e.g. otitis media with effusion).
- Mixed hearing loss refers to the presence of both sensorineural and conductive hearing loss in the same ear. This is the least common form of hearing loss in the pediatric population.
- Auditory neuropathy spectrum disorder (ANDS) is a disorder in which the function of the inner ear is preserved, but the timing (or synchrony) of action potentials in the auditory nerve is disrupted (This finding can be due to a hypoplastic or aplastic cochlear nerve. This result has clinical implications if a cochlear implant is being considered).
- Central auditory processing disorder or central hearing loss may be more common than recognized; prevalence in school-age children has been reported to be 2-3%. These children have difficult understanding speech despite audiometrically normal hearing.
- Hearing loss may be stable, fluctuating and/or progressive
- The severity of hearing loss is commonly divided into five levels:
[Clark: 1981]
- Mild: 20 - 40 dB
- Moderate: 41-55 dB
- Moderately severe: 56-70 dB
- Severe: 71-90 dB
- Profound: >90 dB
- Hearing may may be low frequency, high frequency, predominantly in mid frequencies (“cookie bite”) , or across all frequencies.
- Hearing loss can be unilateral vs. bilateral, symmetrical vs. asymmetrical, or progressive vs. sudden; sudden hearing loss (occurring over <72 hours) should prompt immediate clinical assessment.
Differential Diagnosis
- Language disorder (expressive, receptive, or mixed)
- Autism Spectrum Disorders; see Autism Spectrum Disorder
- Attention deficit disorder, with or without hyperactivity; see Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD)
- Intellectual Disability; see Intellectual Disability & Global Developmental Delay
Medical Conditions Causing Hearing Loss and Deafness
- Congenital Cytomegalovirus (CMV) Related Hearing Loss
- Hearing loss associated with renal disease (Alport syndrome,
Branchio-Oto-Renal syndrome) - Hearing loss syndromes are often associated
with abnormal kidney function/morphology stemming from molecular
similarities between the cochlea and the kidneys.
- Alport Syndrome: A diagnosis of autosomal dominant or X-linked Alport syndrome should be entertained in patients (especially boys) who have sensorineural hearing loss and hereditary nephritis suggested by proteinuria and microscopic hematuria. Consultation with a pediatric nephrologist and geneticist is recommended for individuals with hearing loss and persistent hematuria/proteinuria. Vision may also be affected.
- Branchio-Oto-Renal Syndrome: Children with sensorineural, conductive or mixed hearing loss and branchial arch anomalies (neck masses, branchial cleft cysts or fistulae), should undergo renal ultrasonography to evaluate for anomalies associated with Branchio-Oto-Renal syndrome. Renal anomalies vary in this condition and patients are often asymptomatic. Genetic testing is available and should be coordinated through a geneticist or genetic counselor .
- Usher sydrome - At least 3 distinct types of Usher syndrome have been
described:
- Type 1 is characterized by profound hearing loss, retinitis pigmentosa with onset before age 10 years, and vestibular abnormalities. These children may be delayed in their acquisition of early motor milestones.
- Type 2 displays sloping, high-frequency sensorineural hearing loss, normal vestibular function, and later onset of retinitis pigmentosa than that seen in Type 1 disease.
- Type 3 is characterized by progressive audio-vestibular dysfunction over decades and variable-onset of retinitis pigmentosa. Not every patient with both retinitis pigmentosa and sensorineural hearing loss has Usher syndrome. Some authors have suggested that all children with severe to profound hearing loss should be screened by ophthalmologic exam and electroretinogram for Usher syndrome. In one study of consecutive patients over 2 years of age with severe to profound preverbal hearing loss, 10.4% (5 out of 48) were diagnosed with Usher syndrome after undergoing complete ophthalmologic evaluation that included an electroretinogram. [Mets: 2000]
History & Examination
Current & Past Medical History
- History of prematurity and related complications including administration of aminoglycosides (see Pregnancy and Perinatal History below)
- Serious bacterial infections, such as meningitis (particularly secondary to H. influenza, herpes, and varicella) and sepsis
- Head trauma
- Craniofacial malformations or genetic syndromes that may lead to conductive/mixed hearing loss or Eustachian tube dysfunction (cleft palate, Down syndrome, Turner syndrome, Treacher Collins syndrome, Goldenhar syndrome, Cornelia de Lange syndrome, branchio-oto-renal syndrome)
- Syndromes associated with progressive hearing loss (neurofibromatosis type 2, osteopetrosis, renal tubular acidosis)
- Neurodegenerative disorders, such as Hurler syndrome, Hunter syndrome
- Sensorimotor neuropathies (Charcot-Marie-Tooth syndrome, Friedrich ataxia)
- Syncope, palpitations, history of a possible cardiac arrest (suggesting arrhythmia that could be related to Jervell and Lange-Nielson syndrome)
- Visual impairment, especially retinitis pigmentosa (Usher syndrome)
- Chemotherapy
Family History
Pregnancy/Perinatal History
- Perinatal infections such as bacterial meningitis, cytomegalovirus and sepsis
- NICU stay 5 days or longer
- Hyperbilirubinemia requiring exchange transfusion
- Persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn
- Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO)
- Administration of aminoglycosides or loop diuretics
Developmental & Educational Progress
The Medical Home clinician should conduct routine developmental screening and surveillance at all well child visits. It is also recommended that an early intervention program assess language, cognitive skills, and social-emotional development at 6-month intervals during the first 3 years of life for children who are D/HH. For the older child, close attention should be paid to educational progress, as a decline in academic functioning may signify a progression of hearing loss or poor fit/function of amplification devices.
Social & Family Functioning
Physical Exam
Growth Parameters
Microcephaly and/or short stature may suggest a congenital infection (e.g., CMV, rubella) or underlying genetic disorder. Tall, thin body habitus is associated with Stickler syndrome.
Skin
HEENT/Oral
Assess for craniofacial abnormalities such as wide-spaced eyes (hypertelorism, telecanthus), submucous cleft palate, preauricular tags/pits, and auricular malformations. Pneumatic otoscopy should be performed to assess tympanic membrane mobility and middle ear pressure. Examine the neck for masses, sinuses, and pits and thyroid enlargement (goiter) in older children.
Testing
Sensory Testing
The following tests are commonly used by audiologists to diagnose hearing loss:
- Otoacoustic Emissions (OAE): Sound entering the ear is amplified by the outer hair cells of the cochlea. When outer hair cells are healthy, this amplification produces a pressure wave which is transmitted from the inner ear to the middle ear, called otoacoustic emissions (OAE). Because OAE are preneural in origin, they reflect only the health of the cochlea and cannot be used to assess function of the auditory nerve and brainstem pathways. In testing, frequency-specific clicks are introduced into the ear canal through a small probe and the resulting OAEs are recorded. Middle ear fluid or debris in the external auditory canal can reduce the emissions and cause a falsely abnormal result. A screening OAE gives a Pass or Fail (Refer) result; the latter indicates a need for further hearing assessment. Diagnostic testing with OAE analyzes responses in further detail with interpretation by the audiologist.
- Auditory Brainstem Evoked Responses (AABR or ABR): Sound entering the ear is transduced into action potentials in the brainstem that can be recorded using surface electrodes. Evoked potentials generated in the brainstem are referred to as the auditory brainstem response (ABR). ABR testing evaluates the ability of the inner ear to produce action potentials and their transmission through the auditory nerve and brainstem. Clicks are introduced into the ear canal and EEG signals evoked by the clicks are separated from the background EEG signals, recorded, and analyzed. The automated Auditory Brainstem Evoked Response (AABR), used for newborn screening, employs a statistical algorithm to determine the likelihood that the results reflect normal hearing. Like OAE, the AABR generates a Pass or Fail result; the latter indicates a need for further testing/quantification of hearing. In patients with abnormal AABR results, an audiologist with infant/pediatric expertise should perform a frequency-specific, diagnostic ABR, which can often be performed without sedation in infants under 6 months of age.
-
Audiometry
- In very young infants, typically less than six months of age, behavioral observation is not used to assess hearing sensitivity. [Sabo: 2003] Visual reinforced audiometry (VRA) is the method of choice in children who are developmentally 6 months to 2 years of age. [Gravel: 1992] VRA involves presentation of a sound and rewarding appropriately-timed head turns with a picture or other visual stimulus. [Lidén: 1969] Inserts or headphones can be utilized to obtain ear-specific information, with inserts being preferred to avoid collapsing ear canals. Inserts are more reliably tolerated in children greater than 18 months of age, although a number of pediatric centers have reported excellent success with younger children. [Weiss: 2016] A positive response generally requires a 90-degree head turn, and normative data by age is available for interpretation. [Sabo: 2003]
- Conditioned play audiometry (CPA) may be used with children developmentally 2 to 5 years of age. In this technique, the child is first briefly conditioned to ensure understanding of the task and that they can reliably participate. The chosen task may vary based on child interest and cooperation – for example, putting a peg in a board, tossing a block in a box, or a digital task in response to hearing a sound. [Nielsen: 1997] [Nielsen: 1997]
- Conventional Audiometry: the child indicates that he/she can hear a sound by raising a hand or pressing a button. The threshold, or quietest, level at which the child can detect sounds at various frequencies is measured, allowing the type, degree, and symmetry of a loss to be delineated. Conventional audiometry can usually be performed by the time a child is 3-4 years of age.
- Acoustic Immittance Testing (aka tympanometry) tests middle ear pressure and tympanic membrane compliance and is used to confirm middle ear conditions, such as a fluid-filled middle ear, perforations in the tympanic membrane, and other disorders. Acoustic immittance testing is performed using a hand-held probe with an airtight seal within the ear canal. The probe emits a stimulus tone, which is reflected back to the probe, while the air pressure in the ear canal is changed from negative to positive. The reflected sound is detected by a microphone and quantified to determine the acoustic immittance, which is a measure of the ease of sound flow through the tympanic membrane and the middle ear ossicles. The probe can also measure tympanic membrane mobility, the volume of the ear canal, and the level of sound stimulation required to make the stapedius muscle contract, known as the acoustic reflex threshold.
Laboratory Testing
Children with asymptomatic congenital CMV infection should undergo a diagnostic auditory brainstem response study. If the result is normal, the child still needs to undergo regular hearing screening given the higher risk for late onset and progressive hearing loss.
Imaging
Genetic Testing
Other Testing
Specialty Collaborations & Other Services
Medical Genetics (see NM providers [2])
Genetic Testing and Counseling (see NM providers [6])
Pediatric Otolaryngology (ENT) (see NM providers [11])
Audiology (see NM providers [22])
Pediatric Ophthalmology (see NM providers [6])
Speech - Language Pathologists (see NM providers [23])
Developmental Assessments (see NM providers [105])
Early Intervention for Children with Disabilities/Delays (see NM providers [34])
Special Education/Schools (see NM providers [82])
Treatment & Management
Pearls & Alerts for Treatment & Management
Cochlear implants are approved by the FDA for children 12 months and olderCandidacy for cochlear implant depends on a number of factors including the child’s otologic anatomy, hearing status, caregiver motivation, and support.
Unilateral hearing lossChildren with unilateral hearing loss are at risk for academic failure, experience considerable difficulty in understanding speech in a background of noise, experience trouble with localization (with resulting safety issues), and appear to exhibit more behavioral problems in school. For these reasons, amplification should be used for the affected ear, if possible.
Systems
Ears/Hearing
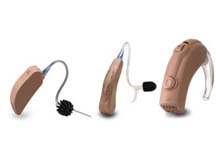
Cochlear implantation may be considered if limited benefit is derived from hearing aids, although at times it is recommended as the primary amplification device. Candidacy depends on a number of factors including the child’s otologic anatomy, hearing status, caregiver motivation and support. Most cochlear centers around the country have a multidisciplinary approach to evaluate candidacy. In general, children between 12 and 18 months of age are candidates if they have profound sensorineural hearing loss (90 decibels or greater) in both ears. Children 18 months of age and older are candidates if they have severe to profound sensorineural hearing loss (70 decibels or greater) in both ears. Children younger than 12 months of age should be considered for early implantation if their profound loss was caused by meningitis, which may cause ossification of the cochlear structures making implantation more difficult later.
Cochlear implants have several internal and external components including an electrode array implanted into the cochlea, a receiver and magnet set into the bone behind the ear, a transmitter coil and a microphone worn behind the ear, and a speech processor carried in a pocket or fanny pack. The microphone receives speech and an electrical signal is sent to the speech processor through a connecting cable. The speech processor converts the electrical signal into a code that has been optimized for speech recognition. This code is then sent back over the cable to the headpiece and transmitted via radio waves to the implanted receiver. The code is then passed to the electrode array that stimulates the afferent auditory neurons within the cochlea. The integrity of the cochlear implant is tested at the time of surgery, immediately after surgery, and during routine follow-up visits. In addition to assuring parents return for ongoing audiologic testing and adjustment, the primary care physician should closely monitor and inquire about the child's language development and school performance during routine well child checks and follow-up appointments.
Bacterial Meningitis Prevention
Children with cochlear implants are at greater risk for bacterial meningitis. This risk can be higher with those with cochleovestibular dysplasias. Streptococcus pneumoniae (pneumococcus) is the major cause of bacterial meningitis in people with cochlear implants. With the widespread use of pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (Prevnar® or "PCV13") and the pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine (Pneumovax® 23 or "PPSV23"), the incidence has decreased dramatically. To reduce the risk of bacterial meningitis, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommend the following vaccinations for individuals with cochlear implants. Please look at the CDC site for recommendations and additional information on vaccination.13-valent pneumococcal conjugate (PCV13) (Prevnar 13®) 23-valent pneumococcal polysaccharide (PPSV23) (Pneumovax®) Haemophilus influenzae type b conjugate (Hib) (ActHIB®, Hiberix®, PedvaxHIB®, and Pentacel®) Meningococcal conjugate (Menactra® and Menveo®) Serogroup B meningococcal (Bexsero® and Trumenba®) There is no evidence that people with cochlear implants are more likely to get meningococcal meningitis (caused by Neisseria meningitidis) than people without cochlear implants.Frequency modulation (FM) auditory trainers use a speaker-worn microphone to transmit amplified speech to a receiver attached to the patient's hearing aid.
Missing issue with id: 3c1f2353.xml may be considered in children who are not candidates for cochlear implantation due to abnormalities of the auditory nerve.
Bone anchored hearing aids amplify sound through bone vibration and are used in children with permanent conductive hearing loss due to external and/or middle ear disorders, malformations, or trauma.
Other surgical intervention – Children with conductive hearing loss due to otitis media with effusion who have normal baseline hearing should be monitored closely with surgical intervention reserved for those with medical or developmental risk factors or significant changes in hearing. Ventilation tubes are the most common surgical procedure to eliminate middle ear fluid and correct persistent otitis media with effusion. Ossicular reconstruction is indicated for ossicular abnormalities from congenital malformations (e.g., malleus fixation) or defects (e.g., cholesteatoma). Closure of congenital perilymphatic fistula can be associated with cochleovestibular dysplasia and may be recommended to prevent recurrent meningitis but may have little impact on ultimate hearing outcome. [Doyle: 2003]
Specialty Collaborations & Other Services
Audiology (see NM providers [22])
Pediatric Otolaryngology (ENT) (see NM providers [11])
Early Intervention for Children with Disabilities/Delays (see NM providers [34])
Development/Language
Specialty Collaborations & Other Services
Early Intervention for Children with Disabilities/Delays (see NM providers [34])
Speech - Language Pathologists (see NM providers [23])
Immunology/Infectious Disease
CMV-related hearing loss is often progressive and may develop after the neonatal period. Fluctuating hearing loss is also common. Children with asymptomatic congenital CMV infection should have hearing screens at birth and regularly through school age to identify and treat hearing loss in a timely manner.
Research supports antiviral treatment of newborns with symptomatic congenital CMV infection to prevent or mitigate sensorineural hearing loss. Current recommendations are to start oral valganciclovir within the first month of life. [Rawlinson: 2017] These children should have serial every 3 month hearing screens starting at birth through age 3, then every 6 months until age 6, then annually afterwards.
In older children, particularly those with a family history of renal failure, consider a urinalysis to assess for hematuria and proteinuria suggestive of Alport syndrome.
Prevention of congenital CMV through prenatal education and hygiene measures has been a hot topic in recent years. Interestingly, the Committee on Practice Bulletins under the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists state that counseling women about prevention of CMV would be difficult to implement because they are impractical or burdensome and that patient instructions are an unproven method to reduce the risk for transmission. [[No: 2015] For more information, see Congenital Cytomegalovirus (CMV) Related Hearing Loss.
Specialty Collaborations & Other Services
Pediatric Infectious Disease (see NM providers [2])
Funding & Access to Care
Some states have hearing aid recycling programs or offer other support for those who cannot independently afford amplification devices. Information about funding assistance can be obtained through local Early Intervention providers, hearing assessment centers, and school hearing programs. Funding for Service Delivery (ASHA) provides additional information regarding potential funding sources for audiology and hearing services. Some state Early Hearing Detection and Intervention (EHDI) programs have additional information regarding help with funding for hearing aids.
Specialty Collaborations & Other Services
Audiology (see NM providers [22])
Special Education/Schools (see NM providers [82])
Early Intervention for Children with Disabilities/Delays (see NM providers [34])
Ask the Specialist
What if my patient has not had newborn screening?
Newborn hearing screening may not be completed with home births or births at centers not offering screening, and occasionally infants will be discharged to home prior to its completion. In these cases, referral should be made for outpatient hearing screening as soon as possible and no later than 1 month of age.
Resources for Clinicians
On the Web
Guidance for clinical follow-up and further testing after a positive newborn screen.
American Academy of Audiology
Resources for professionals who test, treat, and provide care to the deaf or hard of hearing.
Information & Resources on Hearing Loss for Professionals (EHDI-PALS)
Resources for professionals; Early Hearing Detection & Intervention - Pediatric Audiology Links to Services.
Permanent Childhood Hearing Loss (ASHA)
Comprehensive clinical topic review with a focus on family-centered care; American Speech-Language-Hearing Association.
Early Hearing Detection and Intervention (AAP)
Enhances clinical knowledge of the EHDI program and screening guidelines and helps to ensure that newborn screening results
are communicated to families and reported according to state laws. Also has links to state chapters, EHDI experts, and resources;
American Academy of Pediatrics and the Early Hearing Detection and Intervention Program.
Financing and Reimbursement (NCHAM)
Details about clinical coding and paying for interventions for hearing impairment; National Center for Hearing Assessment
and Management.
Hearing Loss in Children (CDC)
Information, statistics, screening/diagnosis, and treatments; from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Helpful Articles
PubMed search for hearing loss or deafness in children, last 1 year
Gifford KA, Holmes MG, Bernstein HH.
Hearing loss in children.
Pediatr Rev.
2009;30(6):207-15; quiz 216.
PubMed abstract
Katbamna B, Crumpton T, Patel DR.
Hearing impairment in children.
Pediatr Clin North Am.
2008;55(5):1175-88, ix.
PubMed abstract
Shearer AE, Smith RJ.
Genetics: advances in genetic testing for deafness.
Curr Opin Pediatr.
2012;24(6):679-86.
PubMed abstract / Full Text
Lieu JEC, Kenna M, Anne S, Davidson L.
Hearing Loss in Children: A Review.
JAMA.
2020;324(21):2195-2205.
PubMed abstract
Clinical Tools
Care Processes & Protocols
Newborn Hearing Screening - Guidelines for the Medical Home (EDHI) ( 85 KB)
85 KB)
Flowchart and information for assuring documentation of normal newborn hearing screening or appropriate follow-up if negative;
Early Hearing Detection & Intervention Program.
Clinical Checklists & Visit Tools
1-3-6 Newborn Hearing Checklist (AAP) ( 105 KB)
105 KB)
Checklist for assuring early detection and intervention for infants born with hearing loss; American Academy of Pediatrics
and the Early Hearing Detection and Intervention Program.
Patient Education & Instructions
'Just in Time' Hearing Resources for Families (NCHAM) ( 574 KB)
574 KB)
A two-page compilation of valuable resources for families with concerns about hearing loss in their child; National Center
for Hearing Assessment and Management.
'Just in Time' Hearing Resources for Families (NCHAM) (Spanish) ( 639 KB)
639 KB)
Two-page compilation of valuable resources for families with concerns about hearing loss in their child; National Center for
Hearing Assessment and Management.
Dietary Supplements and Nutraceuticals for Children with Migraines ( 327 KB)
327 KB)
A summarized list of supplements and suggested dosing recommended by American Headache Society; Texas Childrens.
Resources for Patients & Families
Information on the Web
Parents' Guide to Hearing Loss (CDC)
Website with comprehensive information on hearing loss in children, including intervention options, building language, decision
making, resources, and a glossary of related terms; from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Strategies for Keeping Hearing Aids on Young Children (Success for Children with Hearing Loss)
Age-appropriate tips for keeping and checking hearing aids in babies, toddlers, and preschoolers;
Resources for Parents of Children Who are Deaf or Hard of Hearing (EHDI-PALS)
Information and questions to ask of your hearing and health providers; Early Hearing Detection and Intervention-Pediatric
Audiology Links to Services.
Hearing Tests (My Baby's Hearing)
Overview of hearing testing in children; Boys Town National Research Hospital.
Types of Hearing Loss (My Baby's Hearing)
Answers to questions about the causes of genetic and non-genetic hearing loss in children; sponsored by Boystown National
Research Hospital.
Familiar Sounds Audiogram in English and Spanish ( 381 KB)
381 KB)
Graphic showing normal hearing to profound hearing loss for loudness and pitch. Adapted from the AAP.
Hearing Loss in Children (CDC)
Information, statistics, screening/diagnosis, and treatments; from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Universal Newborn Hearing Screening (My Baby's Hearing)
Information about specific aspects of newborn hearing screening, as well as information for families who have recently received
a diagnosis; Boys Town National Research Hospital.
National & Local Support
American Society for Deaf Children
Independent nonprofit organization whose purpose is to provide support and information to families raising children who are
deaf or hard-of-hearing.
American Speech-Language-Hearing Association
Information for professionals working in audiology, speech-language pathology, and the speech and hearing sciences. Advocate
for people with communication disabilities.
American Academy of Audiology
Resources for professionals who test, treat, and provide care to the deaf or hard of hearing.
Alexander Graham Bell Association
One of the oldest and most comprehensive organizations focused on pediatric hearing loss, including information on how to
find a provider, funding sources and information, scholarships, and a family support section.
Hard of Hearing and Deaf Services (Easter Seals)
Offers a range of services to assist people with hearing loss, including hearing aids, audiology, speech and hearing therapy,
or referral to a specialist. Includes general and state-specific resources.
Family Resources (LCNDEC)
Comprehensive information compiled by deaf adults and educators; provided by the Laurent Clerc National Deaf Education Center
at Gallaudet University.
National Association of the Deaf
National organization whose goal is the cure and prevention of all forms of hearing loss. They also publish a blog and magazine,
provide scholarships, and offer education about disability benefits.
Family Voices
A national, nonprofit, family-led organization promoting quality health care for all children and youth, particularly those
with special health care needs. Locate your Family-to-Family Health Information Center by state.
National Center for Hearing Assessment and Management (NCHAM)
Extensive compilation of resources and support for families with a child who is deaf or hard of hearing.
Studies/Registries
Childhood Hearing Loss (ClinicalTrials.gov)
Studies looking at better understanding, diagnosing, and treating this condition; from the National Library of Medicine.
Otitis Media with Effusion (ClinicalTrials.gov)
Studies looking at better understanding, diagnosing, and treating this condition; from the National Library of Medicine.
Cochlear Implants and Children (ClinicalTrials.gov)
Studies looking at better understanding, diagnosing, and treating this condition; from the National Library of Medicine.
Auditory Brainstem Implants in Children and Adolescents (ClinicalTrial.gov)
Studies looking at better understanding, diagnosing, and treating this condition; from the National Library of Medicine.
Services for Patients & Families in New Mexico (NM)
| Service Categories | # of providers* in: | NM | NW | Other states (3) (show) | | NV | RI | UT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Audiology | 22 | 3 | 8 | 24 | 22 | |||
| Developmental Assessments | 105 | 1 | 5 | 35 | 54 | |||
| Early Intervention for Children with Disabilities/Delays | 34 | 3 | 30 | 13 | 51 | |||
| Genetic Testing and Counseling | 6 | 6 | 12 | 8 | 11 | |||
| Medical Genetics | 2 | 1 | 5 | 4 | 7 | |||
| Pediatric Infectious Disease | 2 | 2 | 4 | 1 | ||||
| Pediatric Ophthalmology | 6 | 1 | 6 | 8 | 4 | |||
| Pediatric Otolaryngology (ENT) | 11 | 1 | 5 | 7 | 10 | |||
| Special Education/Schools | 82 | 3 | 9 | 35 | 43 | |||
| Speech - Language Pathologists | 23 | 4 | 11 | 33 | 65 | |||
For services not listed above, browse our Services categories or search our database.
* number of provider listings may vary by how states categorize services, whether providers are listed by organization or individual, how services are organized in the state, and other factors; Nationwide (NW) providers are generally limited to web-based services, provider locator services, and organizations that serve children from across the nation.
Authors & Reviewers
| Senior Author: | Albert H. Park, MD |
| Reviewer: | John C. Carey, MD |
| 2019: update: Janet W. Lee, MDA; Albert H. Park, MDSA |
| 2018: update: Jennifer Goldman, MD, MRP, FAAPR |
| 2013: first version: Jennifer Goldman, MD, MRP, FAAPA; Terry E. Foust, AuD, CCC-SLPA; Catherine Jolma, MDCA; William Kimberling, Ph.D.CA; Richard Harward, AuDR; Albert H. Park, MDA; John C. Carey, MDR |
Bibliography
[No authors listed].
Practice bulletin no. 151: Cytomegalovirus, parvovirus B19, varicella zoster, and toxoplasmosis in pregnancy.
Obstet Gynecol.
2015;125(6):1510-1525.
PubMed abstract
Alford RL, Arnos KS, Fox M, Lin JW, Palmer CG, Pandya A, Rehm HL, Robin NH, Scott DA, Yoshinaga-Itano C.
American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics guideline for the clinical evaluation and etiologic diagnosis of hearing
loss.
Genet Med.
2014;16(4):347-55.
PubMed abstract
Barsky-Firkser L, Sun S.
Universal newborn hearing screenings: a three-year experience.
Pediatrics.
1997;99(6):E4.
PubMed abstract
Boppana SB, Ross SA, Novak Z, Shimamura M, Tolan RW Jr, Palmer AL, Ahmed A, Michaels MG, Sánchez PJ, Bernstein DI, Britt WJ,
Fowler KB.
Dried blood spot real-time polymerase chain reaction assays to screen newborns for congenital cytomegalovirus infection.
JAMA.
2010;303(14):1375-82.
PubMed abstract / Full Text
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Identifying infants with hearing loss - United States, 1999-2007.
MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep.
2010;59(8):220-3.
PubMed abstract
Clark JG.
Uses and abuses of hearing loss classification.
ASHA.
1981;23(7):493-500.
PubMed abstract
Davis JM, Elfenbein J, Schum R, Bentler RA.
Effects of mild and moderate hearing impairments on language, educational, and psychosocial behavior of children.
J Speech Hear Disord.
1986;51(1):53-62.
PubMed abstract
Dollard SC, Dreon M, Hernandez-Alvarado N, Amin MM, Wong P, Lanzieri TM, Osterholm EA, Sidebottom A, Rosendahl S, McCann MT,
Schleiss MR.
Sensitivity of Dried Blood Spot Testing for Detection of Congenital Cytomegalovirus Infection.
JAMA Pediatr.
2021;175(3):e205441.
PubMed abstract / Full Text
Downie L, Amor DJ, Halliday J, Lewis S, Martyn M, Goranitis I.
Exome Sequencing for Isolated Congenital Hearing Loss: A Cost-Effectiveness Analysis.
Laryngoscope.
2021;131(7):E2371-E2377.
PubMed abstract
Doyle KJ, Ray RM.
The otolaryngologist's role in management of hearing loss in infancy and childhood.
Ment Retard Dev Disabil Res Rev.
2003;9(2):94-102.
PubMed abstract
Finitzo T, Albright K, O'Neal J.
The newborn with hearing loss: detection in the nursery.
Pediatrics.
1998;102(6):1452-60.
PubMed abstract
Gifford KA, Holmes MG, Bernstein HH.
Hearing loss in children.
Pediatr Rev.
2009;30(6):207-15; quiz 216.
PubMed abstract
Goderis J, De Leenheer E, Smets K, Van Hoecke H, Keymeulen A, Dhooge I.
Hearing loss and congenital CMV infection: a systematic review.
Pediatrics.
2014;134(5):972-82.
PubMed abstract
Gravel JS, Traquina DN.
Experience with the audiologic assessment of infants and toddlers.
Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol.
1992;23(1):59-71.
PubMed abstract
Harlor AD Jr, Bower C.
Hearing assessment in infants and children: recommendations beyond neonatal screening.
Pediatrics.
2009;124(4):1252-63.
PubMed abstract / Full Text
Johnson JL, Kuntz NL, Sia CC, White KR, Johnson RL.
Newborn hearing screening in Hawaii.
Hawaii Med J.
1997;56(12):352-5.
PubMed abstract
Joint Committee on Infant Hearing.
Year 2019 position statement: Principles and guidelines for early hearing detection and intervention programs.
Journal of Early Hearing Detection and Intervention.
2019.
/ Full Text
Katbamna B, Crumpton T, Patel DR.
Hearing impairment in children.
Pediatr Clin North Am.
2008;55(5):1175-88, ix.
PubMed abstract
Kennedy C, McCann D, Campbell MJ, Kimm L, Thornton R.
Universal newborn screening for permanent childhood hearing impairment: an 8-year follow-up of a controlled trial.
Lancet.
2005;366(9486):660-2.
PubMed abstract
Kennedy CR, McCann DC, Campbell MJ, Law CM, Mullee M, Petrou S, Watkin P, Worsfold S, Yuen HM, Stevenson J.
Language ability after early detection of permanent childhood hearing impairment.
N Engl J Med.
2006;354(20):2131-41.
PubMed abstract
Lidén G, Kankkunen A.
Visual reinforcement audiometry.
Arch Otolaryngol.
1969;89(6):865-72.
PubMed abstract
Lieu JEC, Kenna M, Anne S, Davidson L.
Hearing Loss in Children: A Review.
JAMA.
2020;324(21):2195-2205.
PubMed abstract
Liming BJ, Carter J, Cheng A, Choo D, Curotta J, Carvalho D, Germiller JA, Hone S, Kenna MA, Loundon N, Preciado D, Schilder
A, Reilly BJ, Roman S, Strychowsky J, Triglia JM, Young N, Smith RJ.
International Pediatric Otolaryngology Group (IPOG) consensus recommendations: Hearing loss in the pediatric patient.
Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol.
2016;90:251-258.
PubMed abstract
Expert opinion by the members of the International Pediatric Otolaryngology Group on the workup of hearing loss in the pediatric
patient.
Linden Phillips L, Bitner-Glindzicz M, Lench N, Steel KP, Langford C, Dawson SJ, Davis A, Simpson S, Packer C.
The future role of genetic screening to detect newborns at risk of childhood-onset hearing loss.
Int J Audiol.
2013;52(2):124-33.
PubMed abstract / Full Text
Mafong DD, Shin EJ, Lalwani AK.
Use of laboratory evaluation and radiologic imaging in the diagnostic evaluation of children with sensorineural hearing loss.
Laryngoscope.
2002;112(1):1-7.
PubMed abstract
Mehl AL, Thomson V.
Newborn hearing screening: the great omission.
Pediatrics.
1998;101(1):E4.
PubMed abstract
Mehra S, Eavey RD, Keamy DG Jr.
The epidemiology of hearing impairment in the United States: newborns, children, and adolescents.
Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg.
2009;140(4):461-72.
PubMed abstract
Mehta D, Noon SE, Schwartz E, Wilkens A, Bedoukian EC, Scarano I, Crenshaw EB 3rd, Krantz ID.
Outcomes of evaluation and testing of 660 individuals with hearing loss in a pediatric genetics of hearing loss clinic.
Am J Med Genet A.
2016;170(10):2523-30.
PubMed abstract
Mets MB, Young NM, Pass A, Lasky JB.
Early diagnosis of Usher syndrome in children.
Trans Am Ophthalmol Soc.
2000;98:237-42; discussion 243-5.
PubMed abstract / Full Text
Moeller MP.
Early intervention and language development in children who are deaf and hard of hearing.
Pediatrics.
2000;106(3):E43.
PubMed abstract
Moller A.
Hearing: Anatomy, Physiology, and Disorders of the Auditory System.
3rd ed. San Diego: Plural Publishing;
2012.
978-1597564274
Nielsen SE, Olsen SO.
Validation of play-conditioned audiometry in a clinical setting.
Scand Audiol.
1997;26(3):187-91.
PubMed abstract
Rawlinson WD, Boppana SB, Fowler KB, Kimberlin DW, Lazzarotto T, Alain S, Daly K, Doutré S, Gibson L, Giles ML, Greenlee J,
Hamilton ST, Harrison GJ, Hui L, Jones CA, Palasanthiran P, Schleiss MR, Shand AW, van Zuylen WJ.
Congenital cytomegalovirus infection in pregnancy and the neonate: consensus recommendations for prevention, diagnosis, and
therapy.
Lancet Infect Dis.
2017;17(6):e177-e188.
PubMed abstract
Sabo DL, Paradise JL, Kurs-Lasky M, Smith CG.
Hearing levels in infants and young children in relation to testing technique, age group, and the presence or absence of middle-ear
effusion.
Ear Hear.
2003;24(1):38-47.
PubMed abstract
Shearer AE, Smith RJ.
Genetics: advances in genetic testing for deafness.
Curr Opin Pediatr.
2012;24(6):679-86.
PubMed abstract / Full Text
US Preventive Services Task Force.
Universal screening for hearing loss in newborns: US Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement.
Pediatrics.
2008;122(1):143-8.
PubMed abstract
Watkin P, McCann D, Law C, Mullee M, Petrou S, Stevenson J, Worsfold S, Yuen HM, Kennedy C.
Language ability in children with permanent hearing impairment: the influence of early management and family participation.
Pediatrics.
2007;120(3):e694-701.
PubMed abstract
Weiss AD, Karzon RK, Ead B, Lieu JE.
Efficacy of earphones for 12- to 24-month-old children during visual reinforcement audiometry.
Int J Audiol.
2016;55(4):248-53.
PubMed abstract
Yoshinaga-Itano C, Sedey AL, Coulter DK, Mehl AL.
Language of early- and later-identified children with hearing loss.
Pediatrics.
1998;102(5):1161-71.
PubMed abstract


 Get Help in New Mexico
Get Help in New Mexico